Understanding Cavities and Dental Health
What are Cavities?
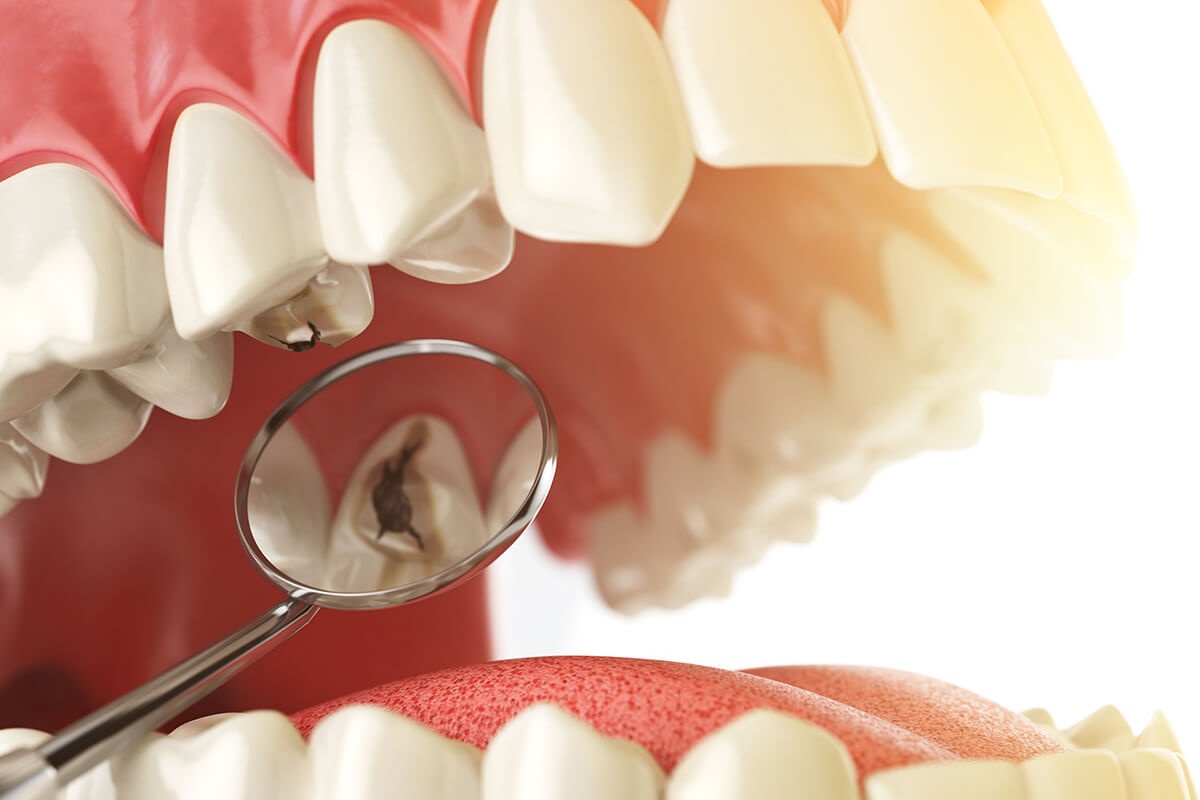
Cavities, also known as dental caries or tooth decay, are a common dental problem affecting people of all ages. They occur when bacteria in the mouth produce acids that erode the enamel of the teeth, leading to the formation of small holes or cavities. If left untreated, cavities can cause pain, infection, and even tooth loss.
Causes of Cavities
Several factors contribute to the development of cavities:
1. Poor Oral Hygiene
Not brushing and flossing regularly allows plaque to build up on the teeth. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that produces acids, leading to enamel erosion and cavity formation.
2. Sugary and Acidic Foods
Consuming foods and beverages high in sugar and acids increases the risk of cavities. Sugars and acids feed the bacteria in the mouth, accelerating the process of tooth decay.
3. Dry Mouth
Saliva helps neutralize acids in the mouth and wash away food particles. A dry mouth lacks sufficient saliva, making it more prone to cavities.
4. Genetics
Genetics play a role in determining the strength of tooth enamel and the risk of cavities. Some people may inherit weaker enamel, making them more susceptible to decay.
Assessing Your Risk for Cavities
While anyone can develop cavities, certain factors may increase your risk:
- Age: Children and older adults are more prone to cavities.
- Diet: A diet high in sugary and acidic foods contributes to cavity formation.
- Oral Hygiene Habits: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to accumulate, increasing the risk of cavities.
- Dry Mouth: Certain medications and medical conditions can cause dry mouth, elevating the risk of cavities.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as acid reflux and eating disorders can expose the teeth to excess acids, promoting decay.
- Genetics: Family history of dental problems may increase susceptibility to cavities.
Preventing Cavities
Taking proactive measures can help prevent cavities and maintain good dental health:
1. Brush and Floss Regularly
Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily to remove plaque and food particles.
2. Limit Sugary and Acidic Foods
Reduce consumption of sugary snacks and beverages, and rinse your mouth with water after consuming acidic foods.
3. Visit Your Dentist Regularly
Schedule regular dental check-ups and cleanings to detect cavities early and receive professional treatment.
4. Use Fluoride Products
Fluoride strengthens tooth enamel and helps prevent cavities. Use fluoride toothpaste and consider fluoride treatments as recommended by your dentist.
5. Consider Dental Sealants
Dental sealants are thin protective coatings applied to the chewing surfaces of the back teeth to prevent decay in the pits and fissures.
Conclusion
Cavities are a common dental concern that can be prevented with proper oral hygiene and regular dental care. Understanding the causes and risk factors for cavities allows individuals to take proactive steps to maintain optimal dental health. By adopting healthy habits and seeking professional dental care, you can reduce your risk of cavities and enjoy a beautiful, healthy smile for years to come.
 Now
Now