Understanding Receding Gums
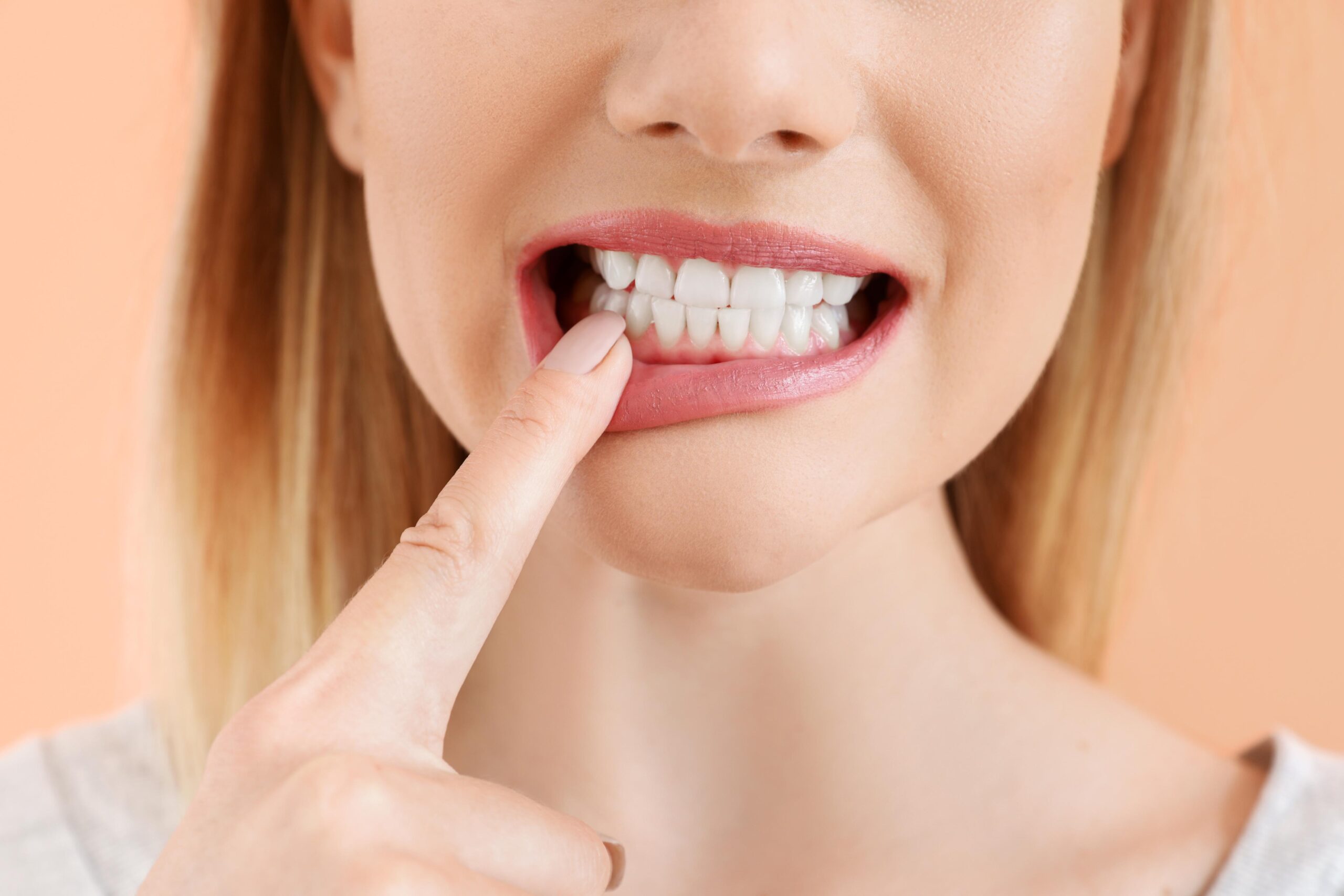
When it comes to dental health, one of the common concerns people face is receding gums. But what exactly are receding gums? Receding gums refer to the condition where the gum tissue that surrounds the teeth wears away or pulls back, exposing more of the tooth or the tooth’s root. This can lead to tooth sensitivity, increased risk of decay, and even tooth loss if not addressed promptly.
Causes of Receding Gums
Several factors contribute to receding gums. One primary cause is poor oral hygiene practices. Not brushing and flossing regularly can allow plaque to build up along the gumline, leading to gum recession over time. Brushing too hard or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can also contribute to gum recession by wearing down the gum tissue.
Other causes include:
Periodontal Diseases
Periodontal diseases such as gingivitis and periodontitis can cause the gums to recede. These conditions involve bacterial infections that attack the gums and bone supporting the teeth, leading to inflammation and eventual gum recession if left untreated.
Genetics
Some people may be genetically predisposed to having thinner or weaker gum tissue, making them more susceptible to gum recession even with proper oral care.
Can Receding Gums Heal?
The good news is that in some cases, receding gums can be treated and even reversed, especially if caught early. However, the extent of healing depends on various factors such as the underlying cause, the severity of the recession, and how well the individual responds to treatment.
Treatment Options
- Improved Oral Hygiene: The first step in treating receding gums is to improve oral hygiene habits. This includes brushing gently with a soft-bristled toothbrush, flossing daily, and using an antiseptic mouthwash to reduce plaque and bacteria buildup.
- Professional Cleanings: Regular dental cleanings by a dental hygienist can help remove plaque and tartar buildup that may contribute to gum recession.
- Scaling and Root Planing: For more advanced cases of gum disease, a deep cleaning procedure called scaling and root planing may be necessary. This involves removing plaque and tartar from the teeth and smoothing out the roots to help the gums reattach to the teeth.
- Gum Grafting: In severe cases where the gum tissue has receded significantly, a gum grafting procedure may be recommended. During this procedure, tissue from another part of the mouth is used to cover exposed tooth roots and help restore the gumline.
Prevention Is Key
While receding gums can be treated, prevention is always the best approach. Practicing good oral hygiene, visiting the dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings, and avoiding habits such as smoking can help reduce the risk of gum recession.
Conclusion
In conclusion, receding gums are a common dental issue that can lead to various oral health problems if left untreated. However, with proper care and treatment, it is possible to prevent further recession and even reverse some of the damage. Remember to prioritize your oral health by maintaining good oral hygiene habits and seeking professional dental care when needed. With the right approach, you can keep your gums healthy and your smile bright for years to come.
 Now
Now